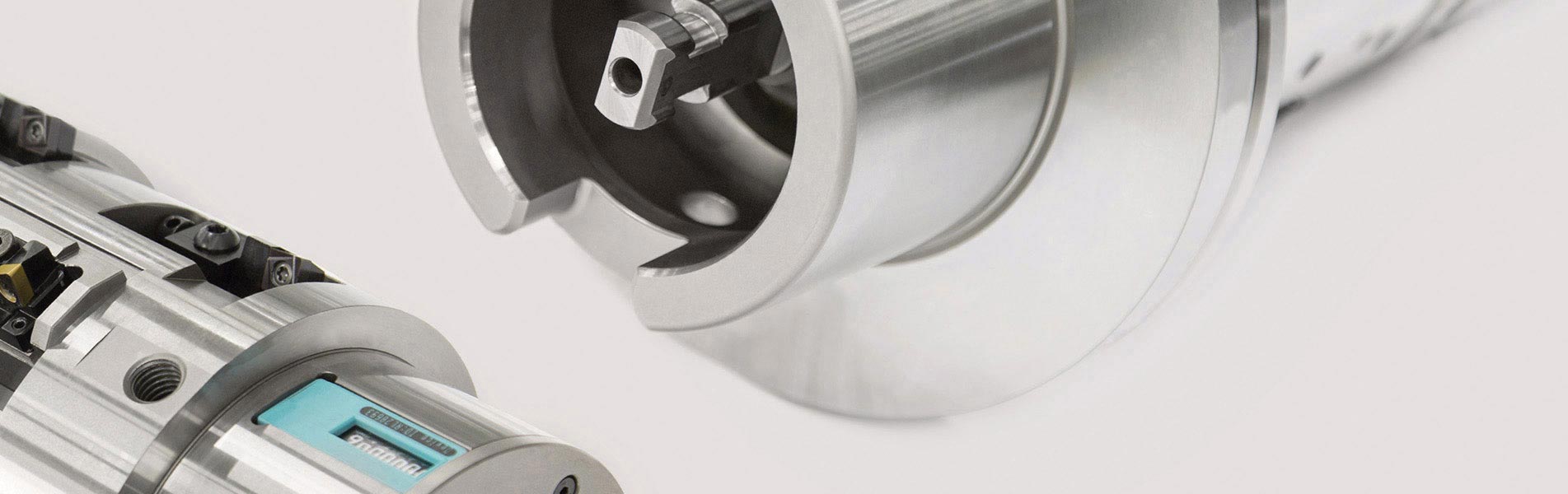
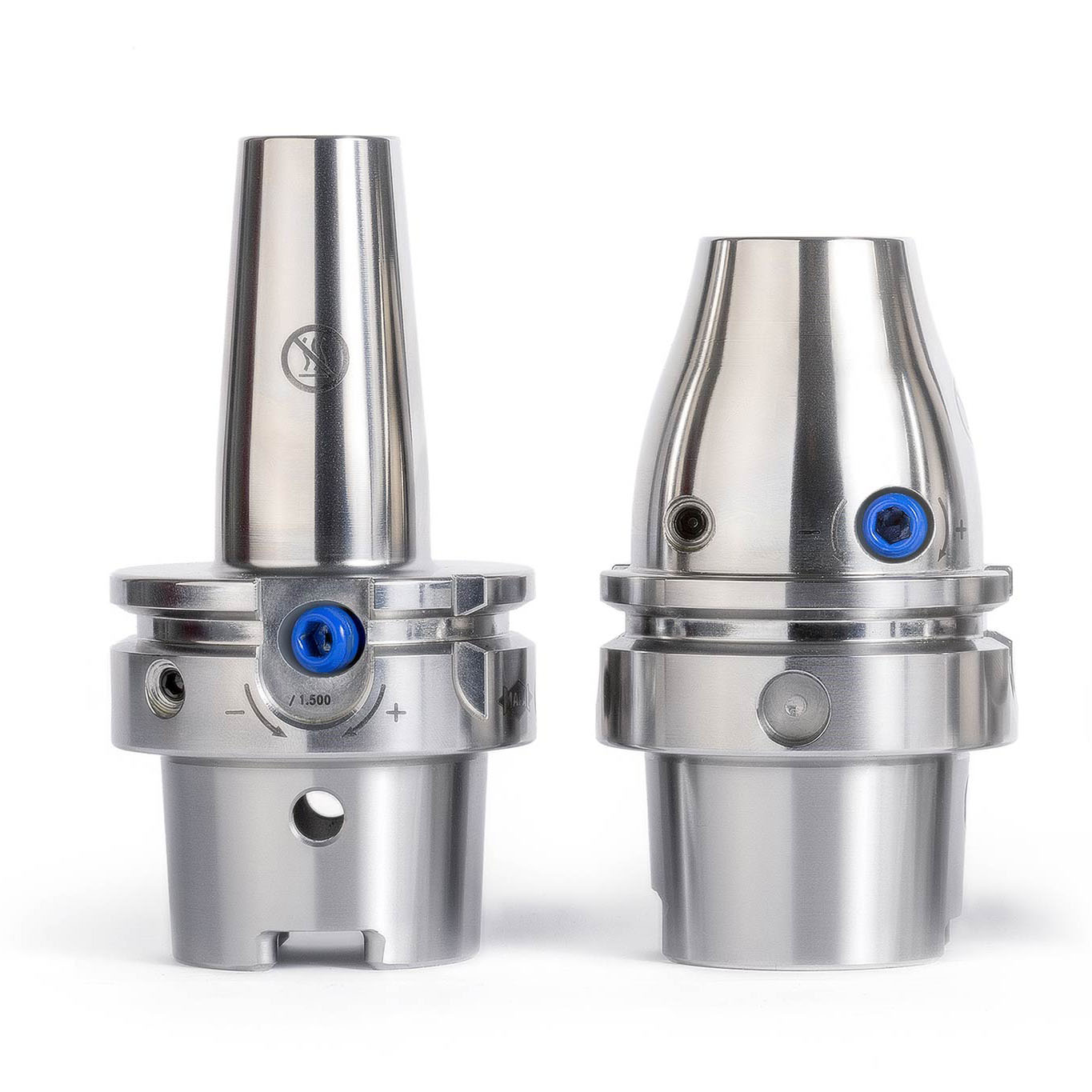
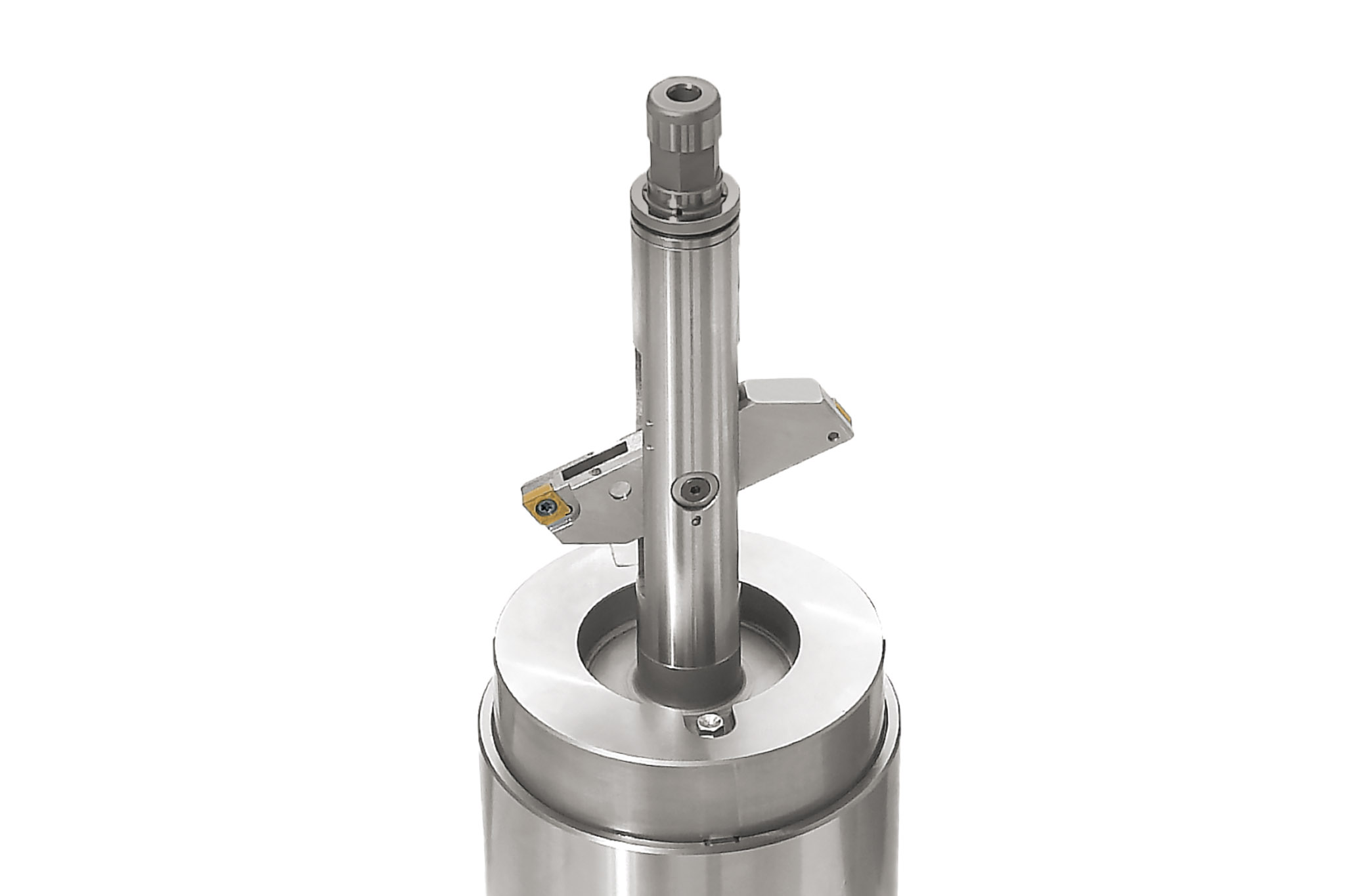
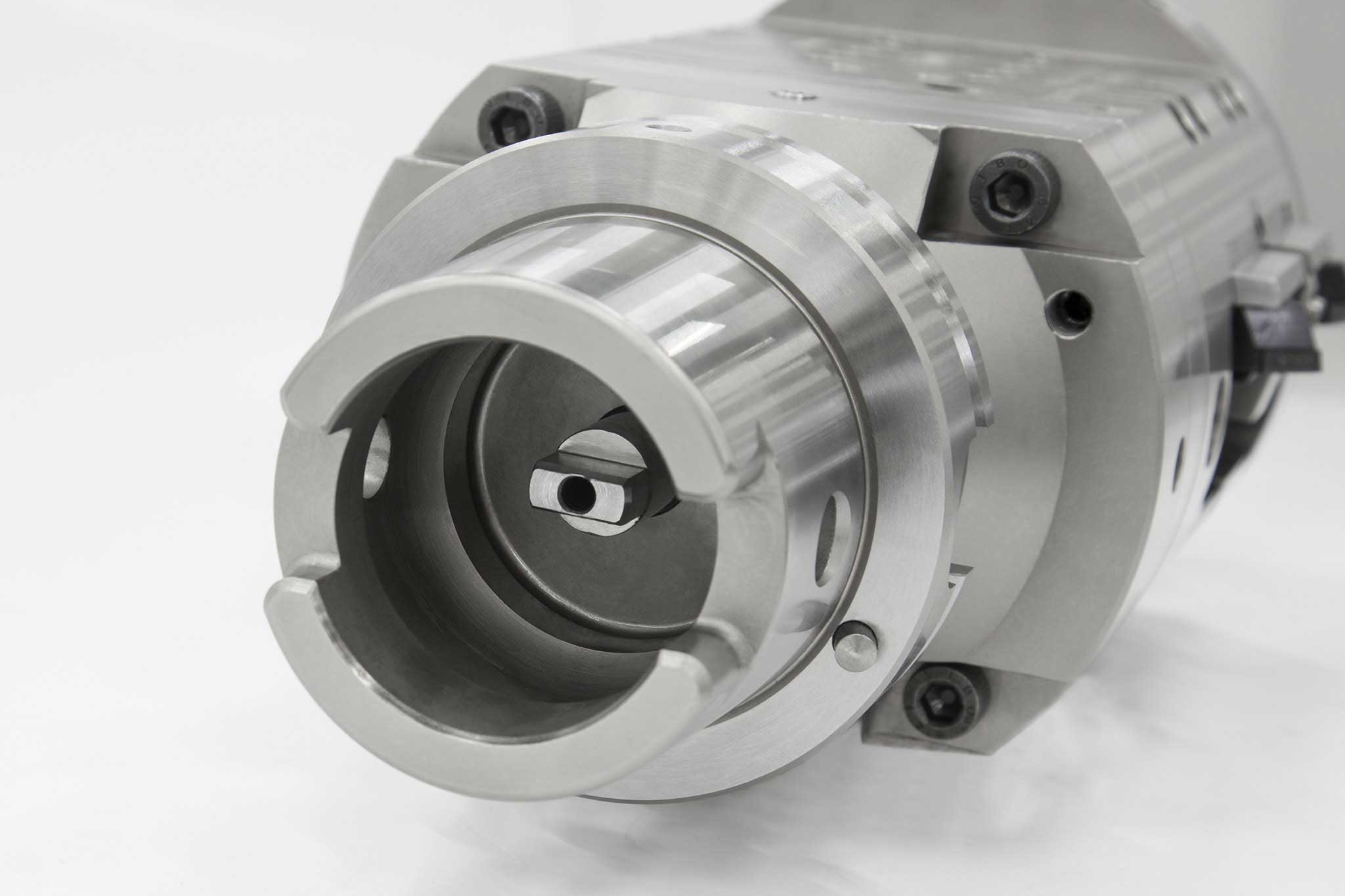
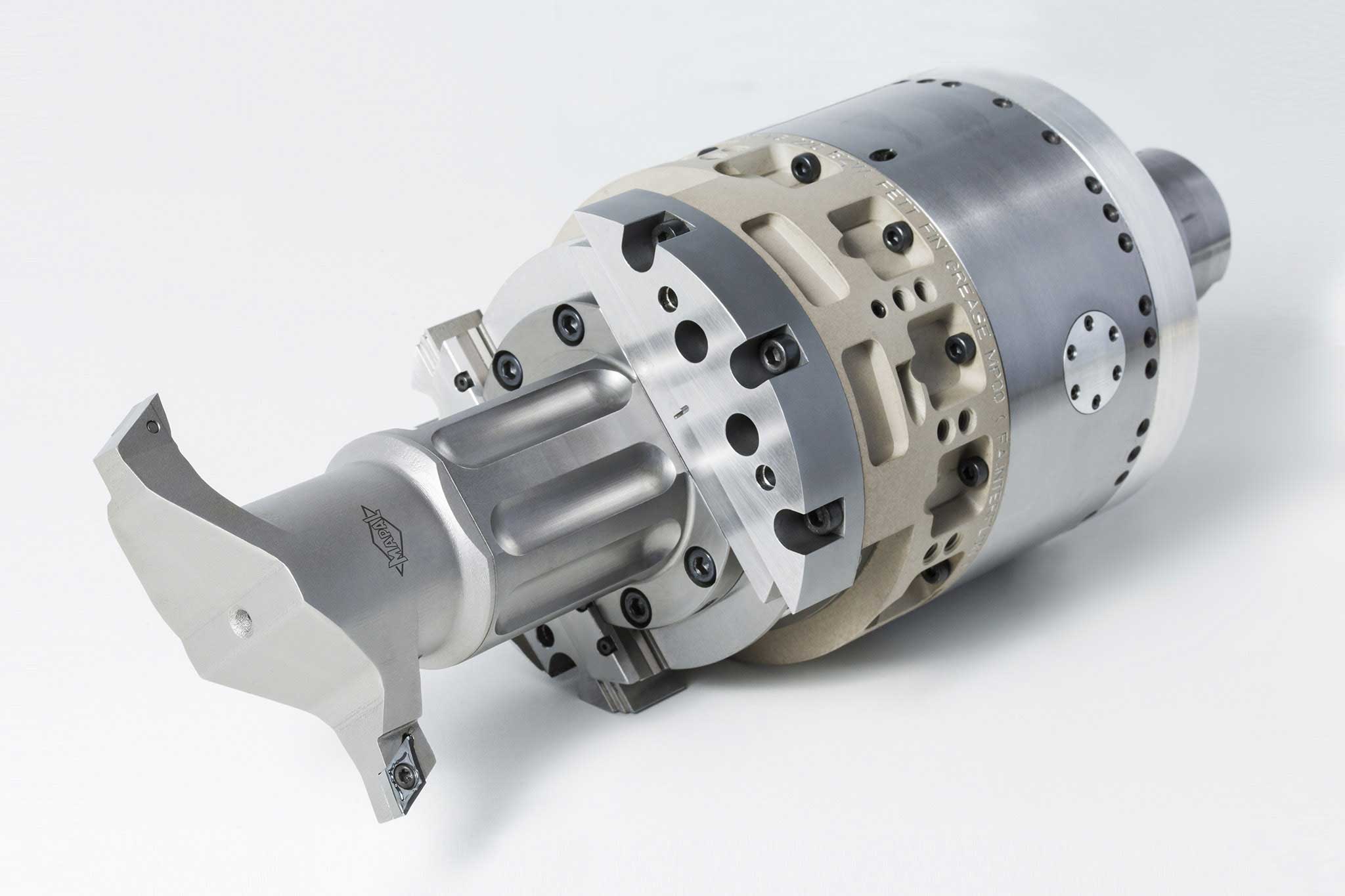
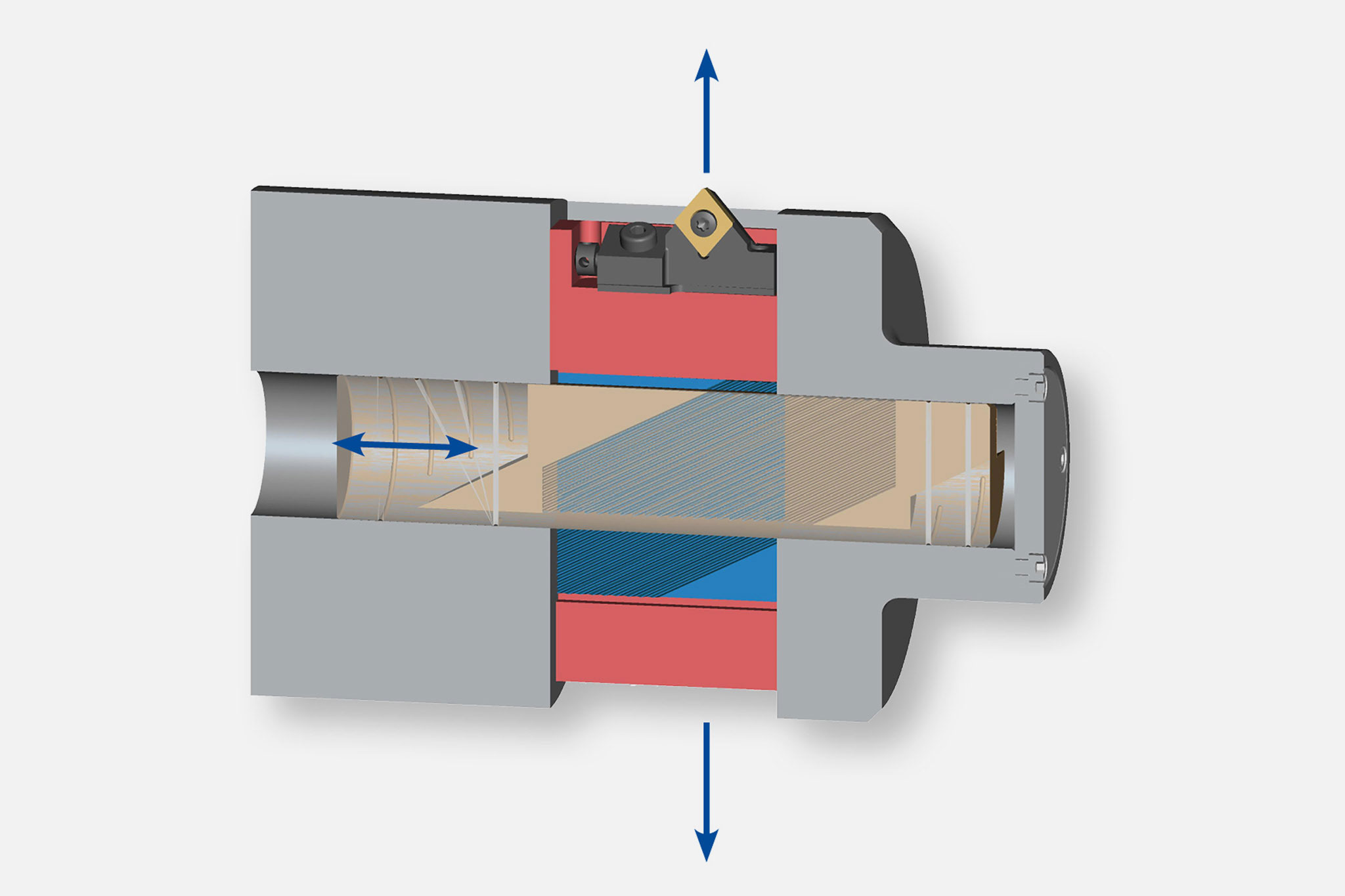
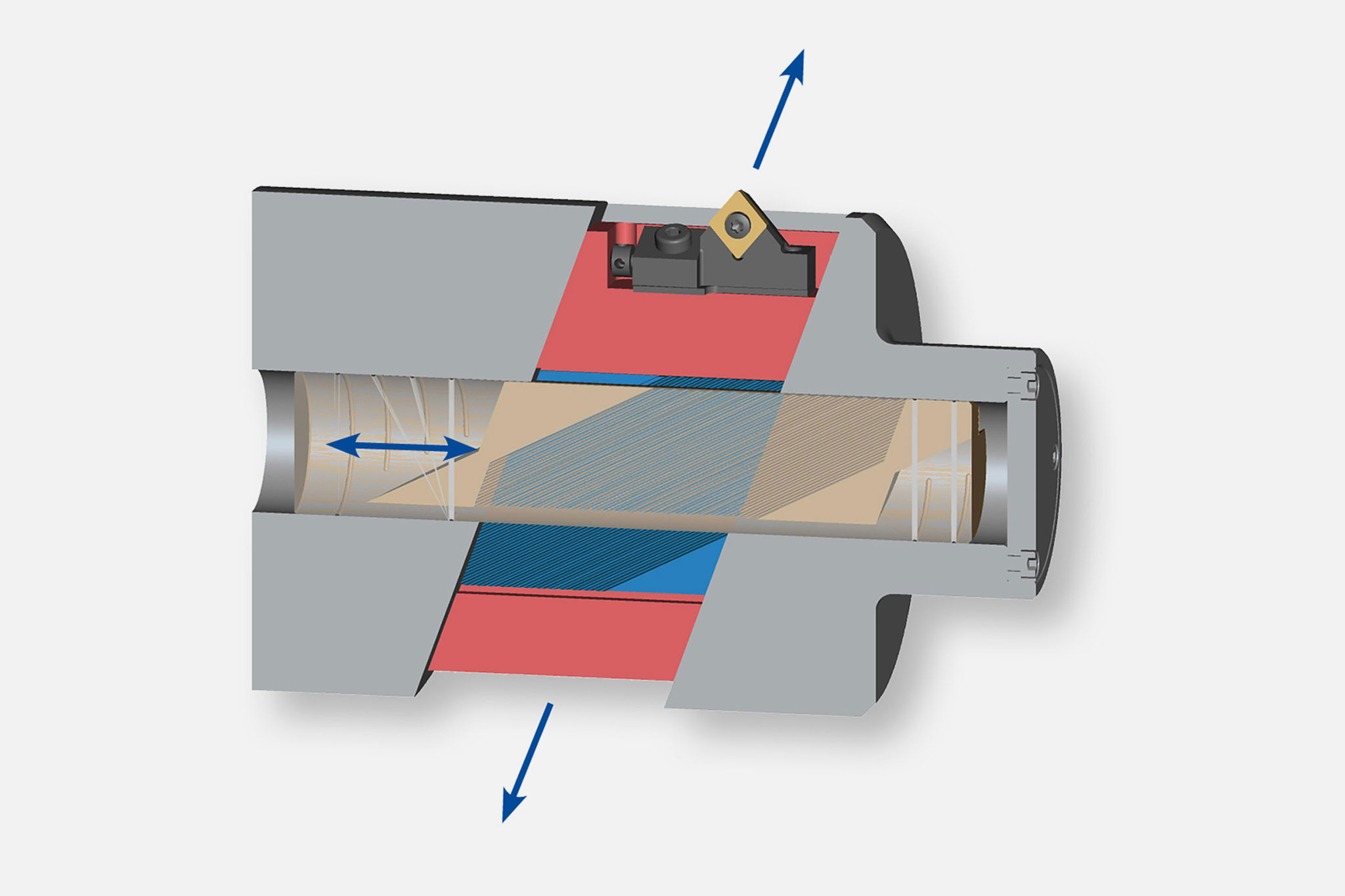
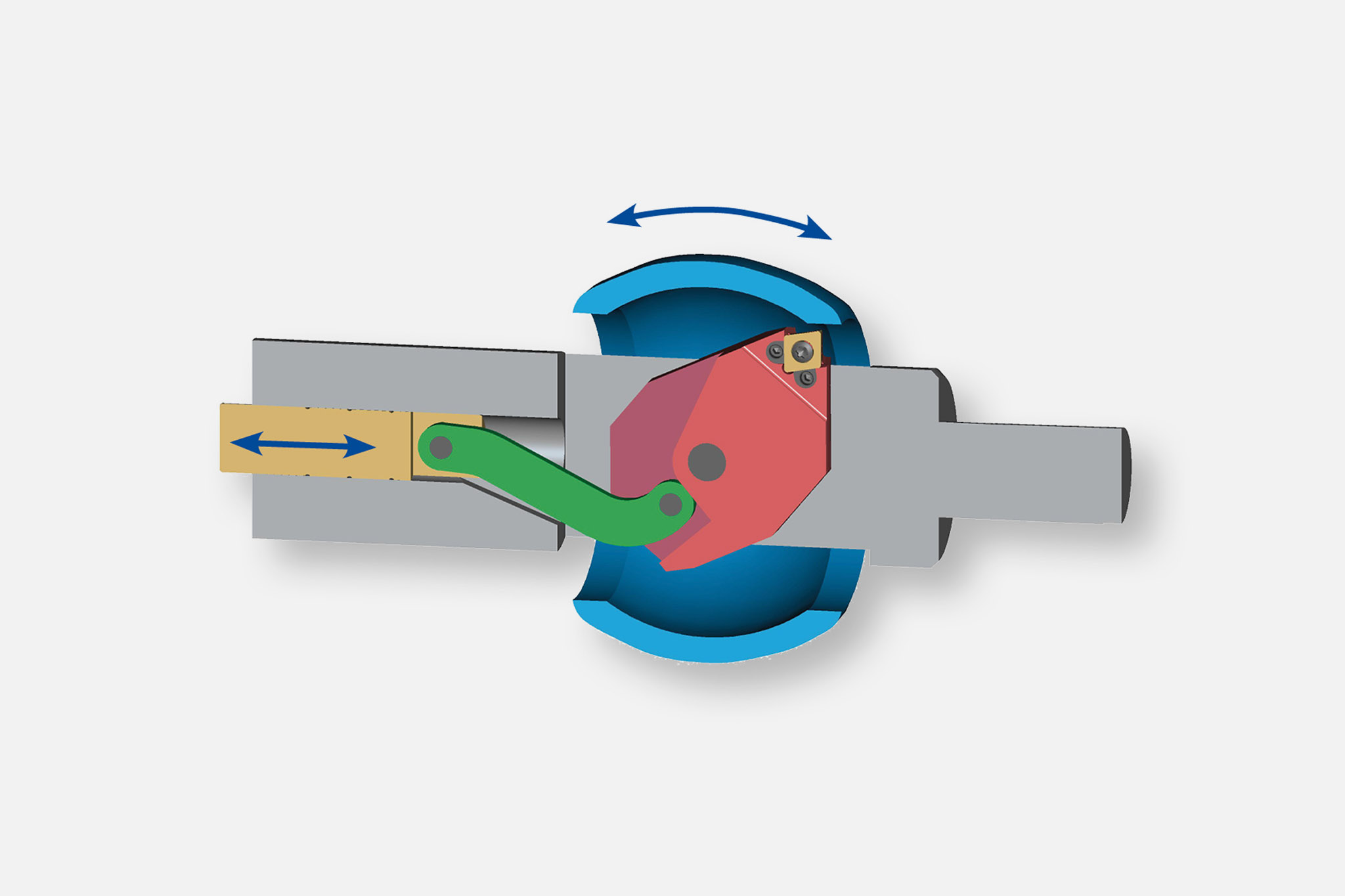
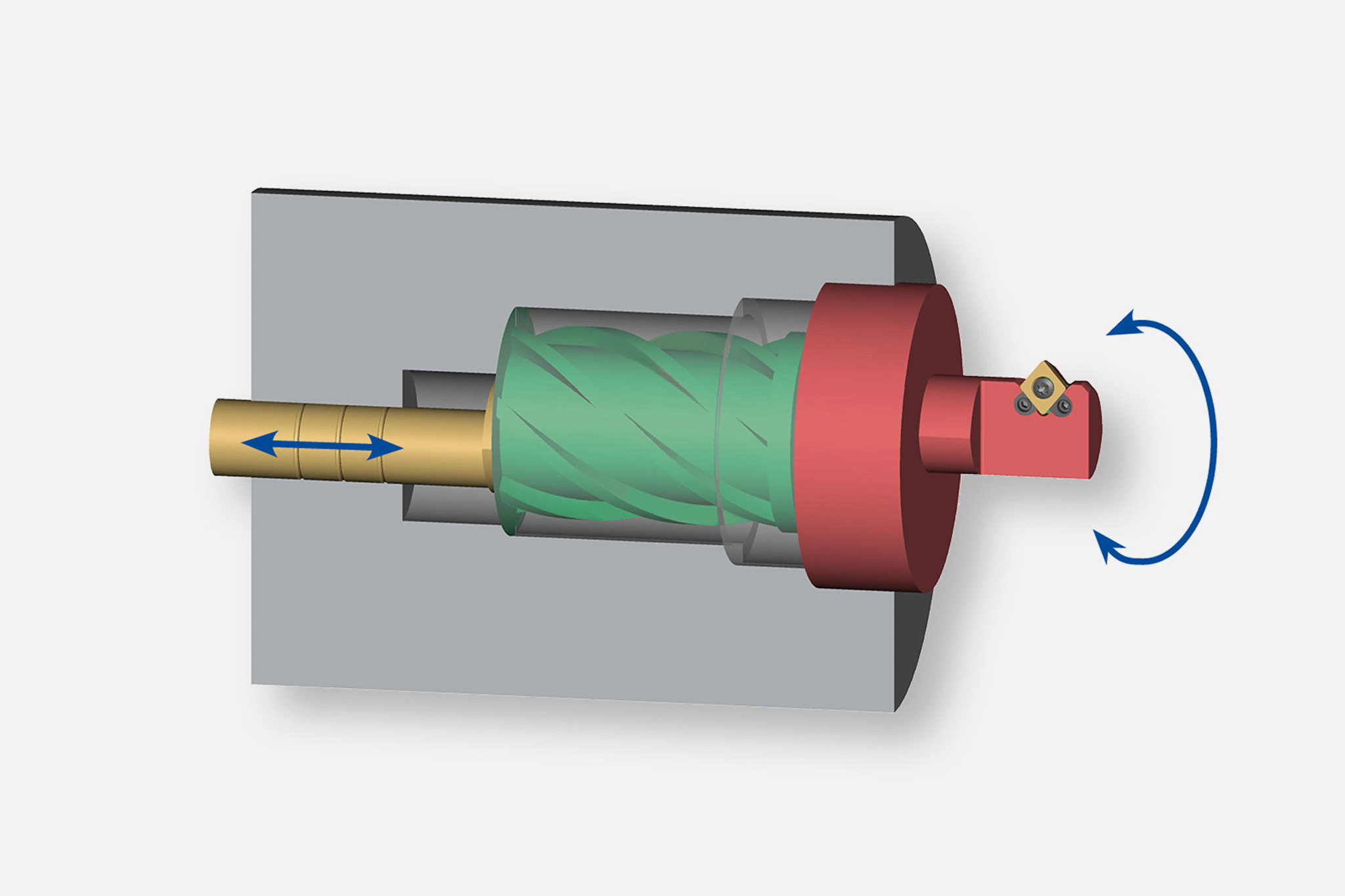
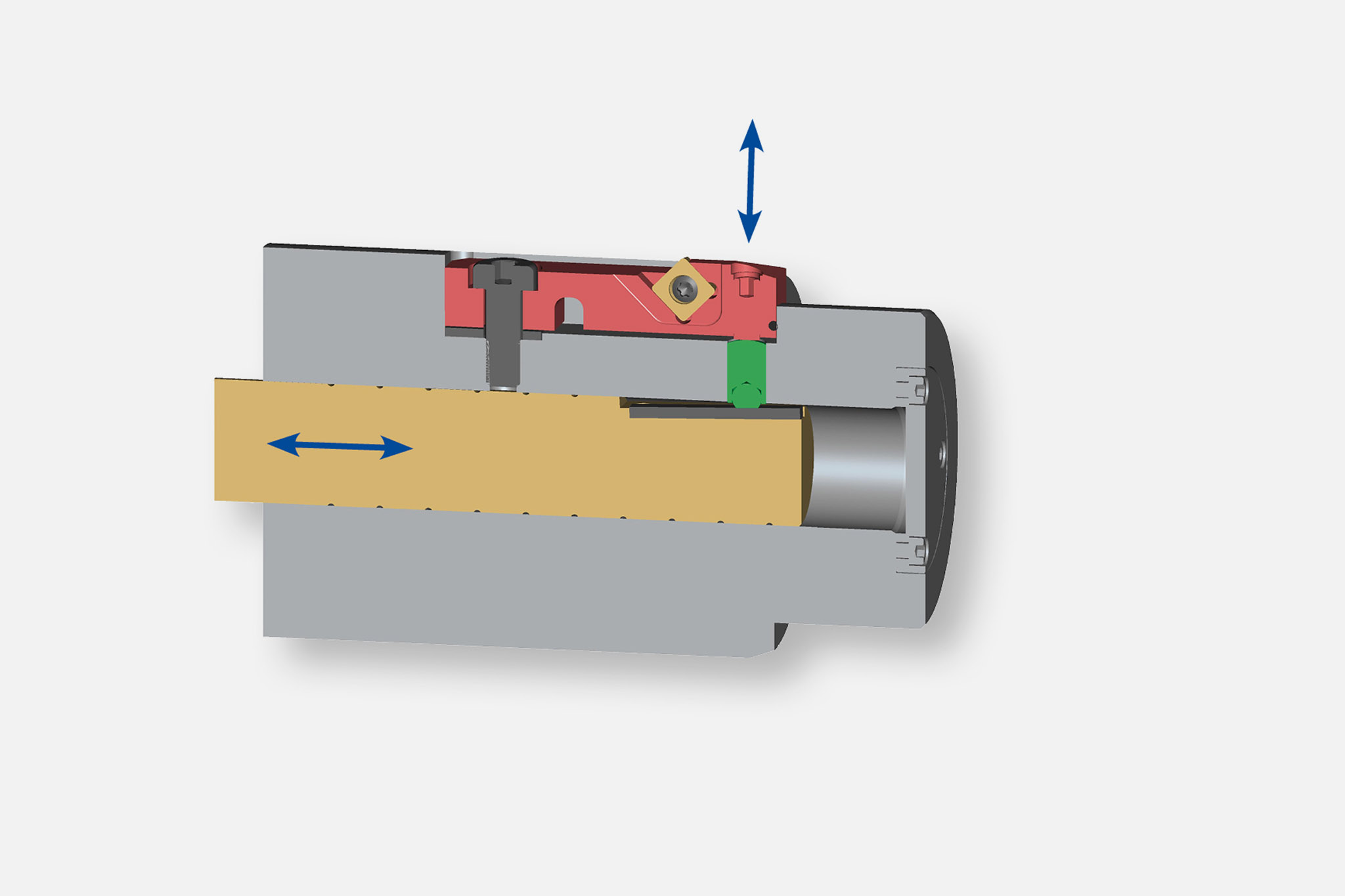
Types of input and output
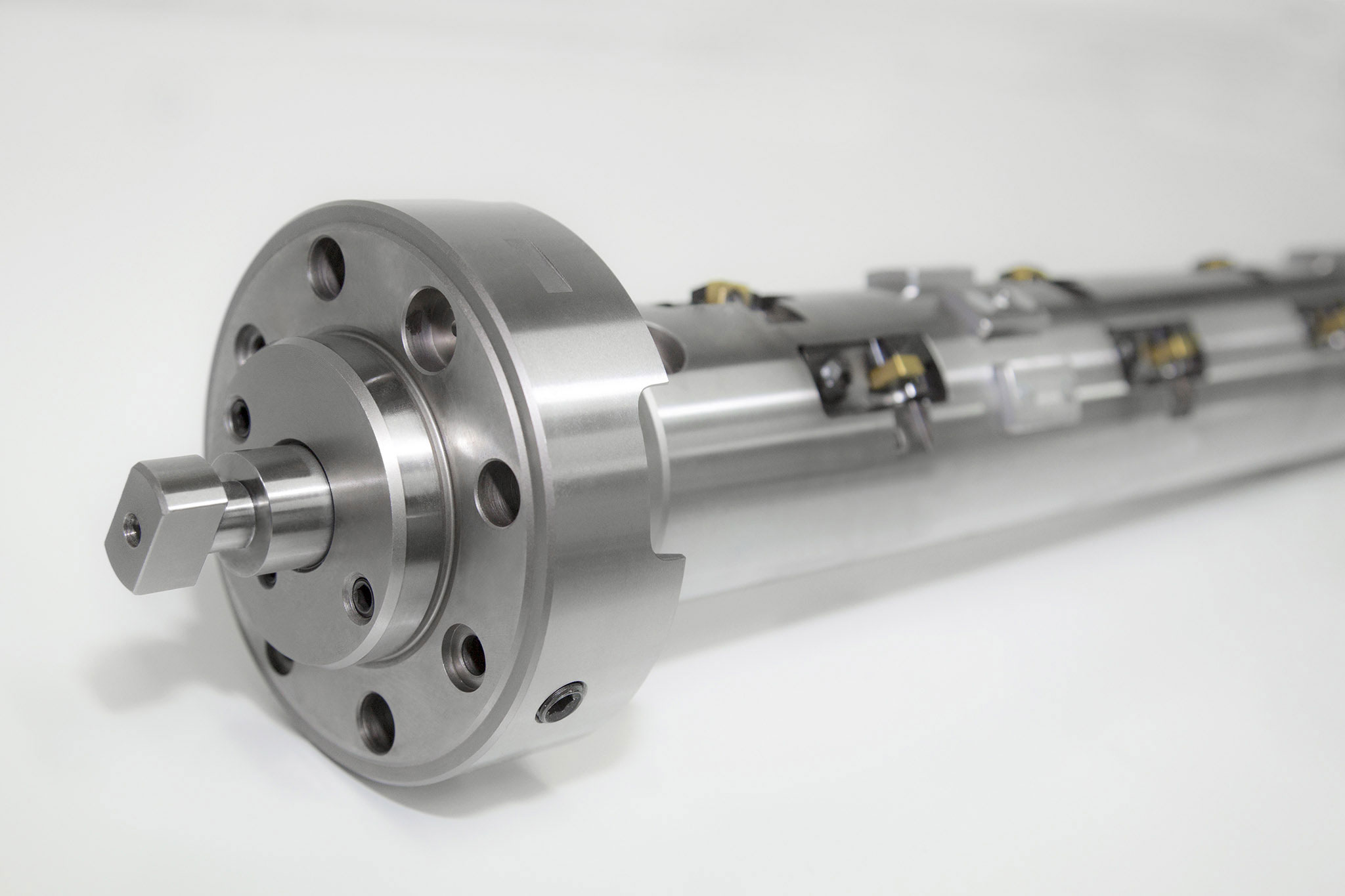
MAPAL uses five different types of input to link actuating tools and the machine tool. In addition to the machine type (machining center or special machine), the decisive factor is whether the machine used has a control function or not.
Six types of output are divided into the areas of 'moving and controlling' as well as 'compensating and lifting'.
A wide range of possible combinations result from these types of input and output. The most suitable combination is selected in close coordination between the MAPAL product specialists and the customer.
Six types of output are divided into the areas of 'moving and controlling' as well as 'compensating and lifting'.
A wide range of possible combinations result from these types of input and output. The most suitable combination is selected in close coordination between the MAPAL product specialists and the customer.