TOOLTRONIC e teste a sfacciare
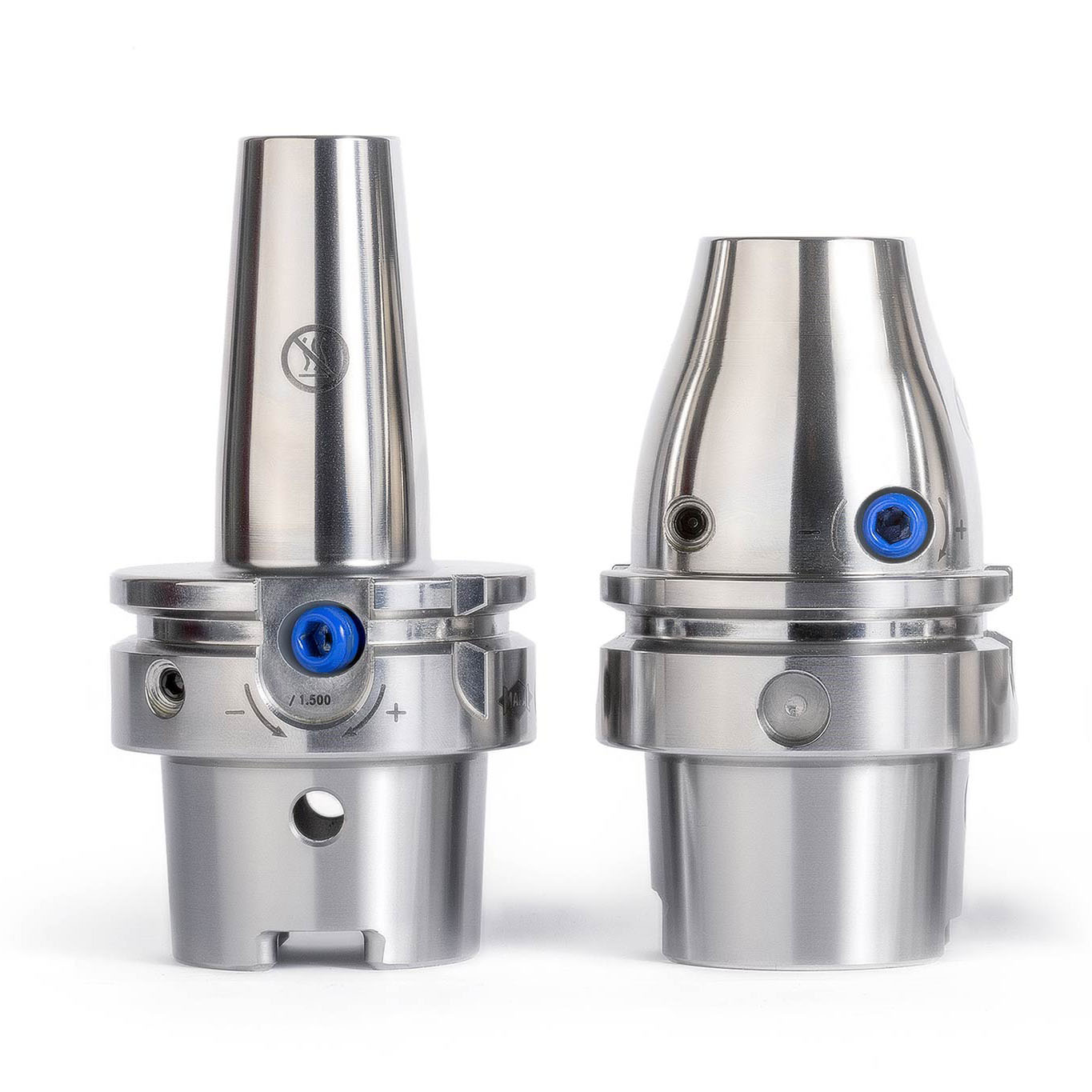
TOOLTRONIC – L'input drive universale per più varietà di lavorazioni e maggiore flessibilità in centri di lavorazione e macchine speciali. Il TOOLTRONIC per centri di lavorazione è una preziosa linea utensile sostituibile, che copre una vasta gamma di impieghi.
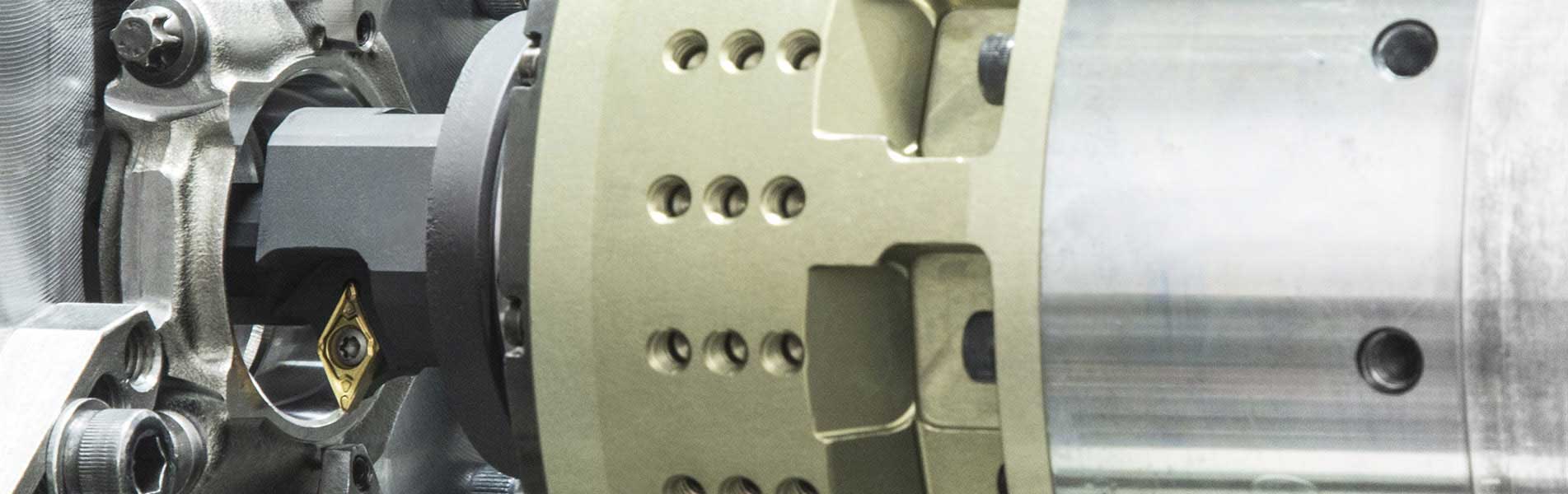
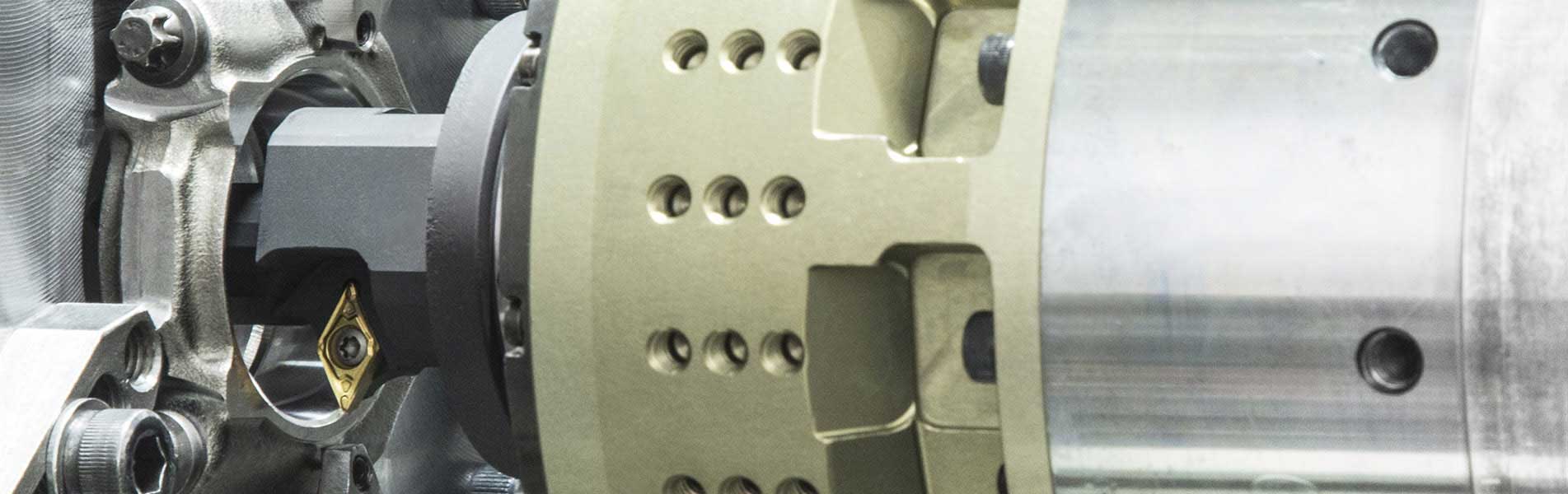
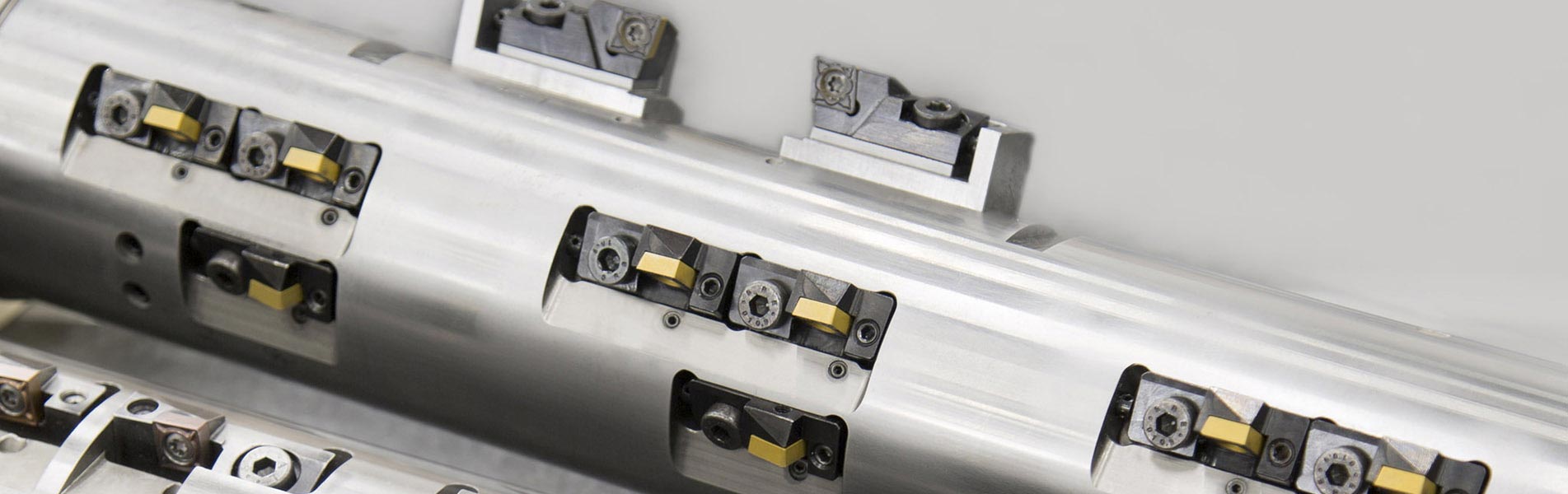
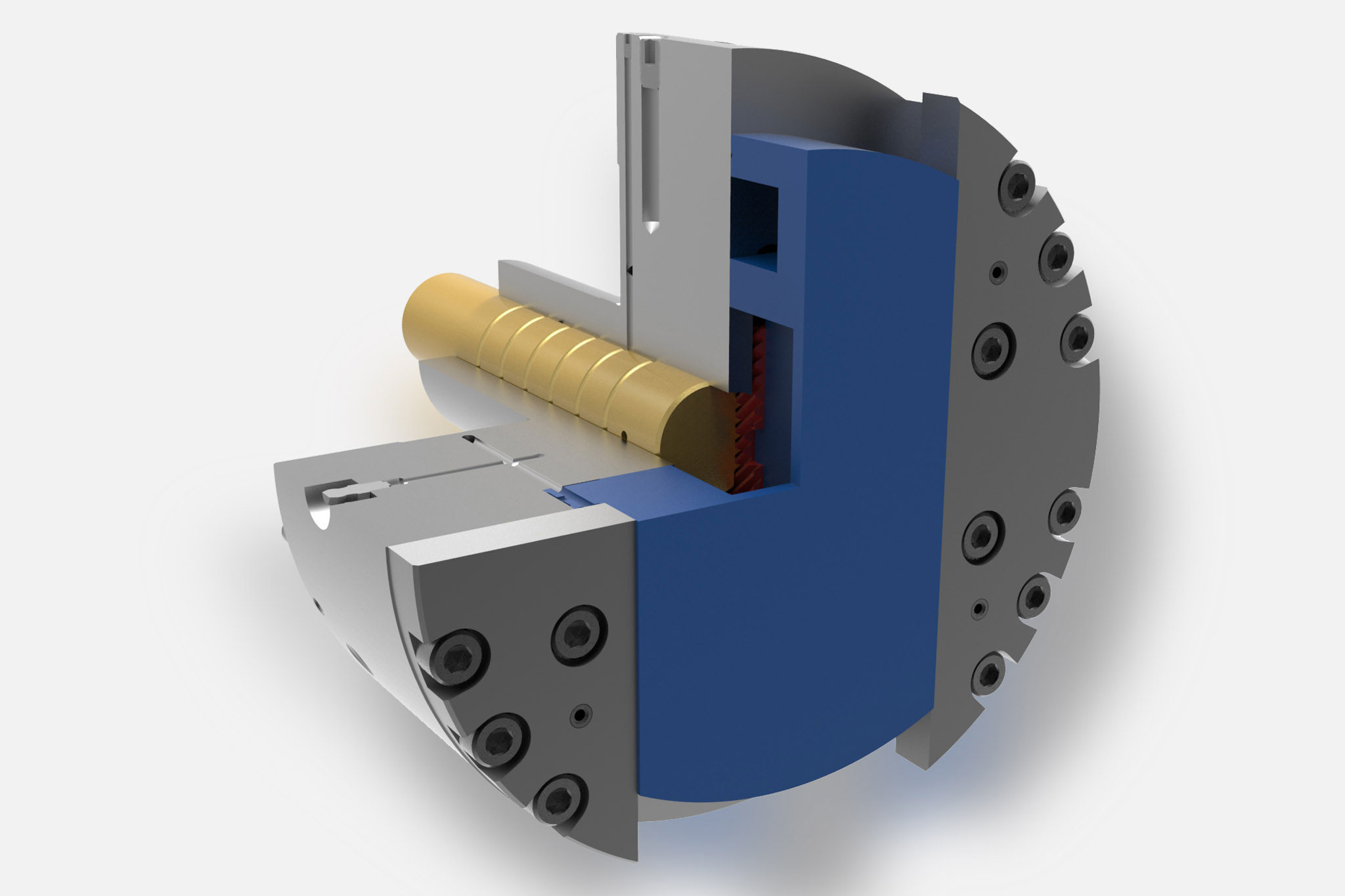
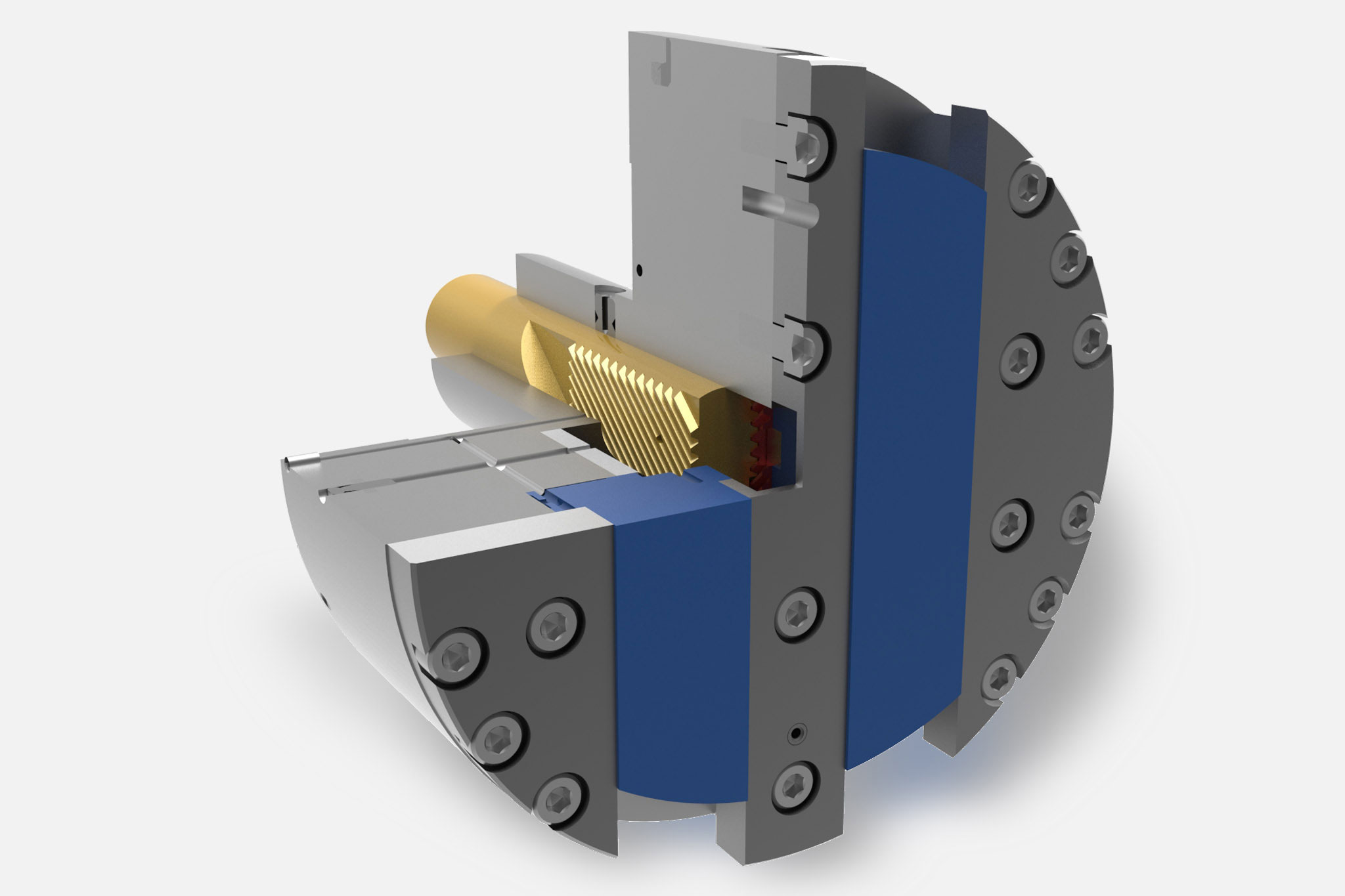
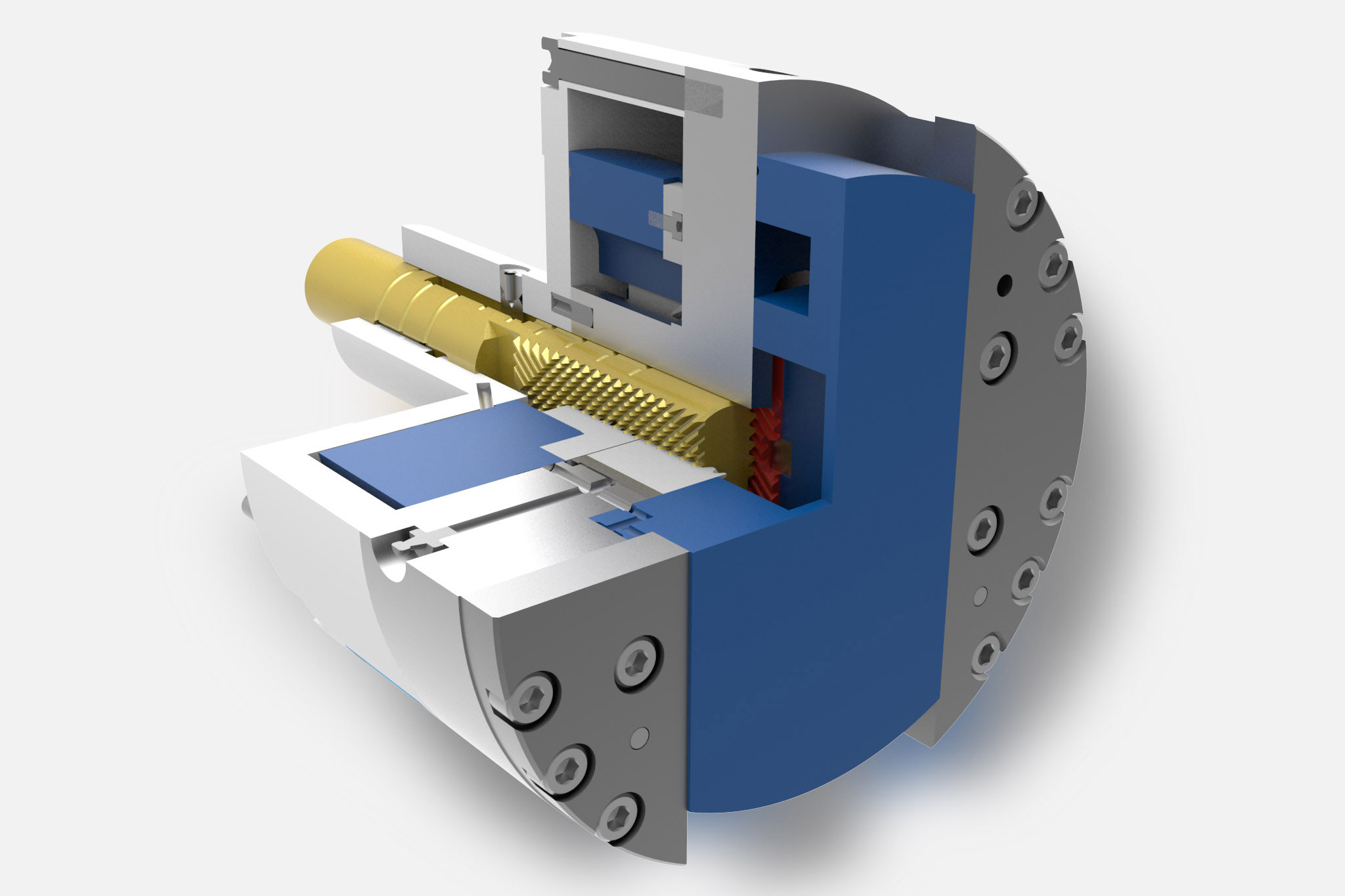
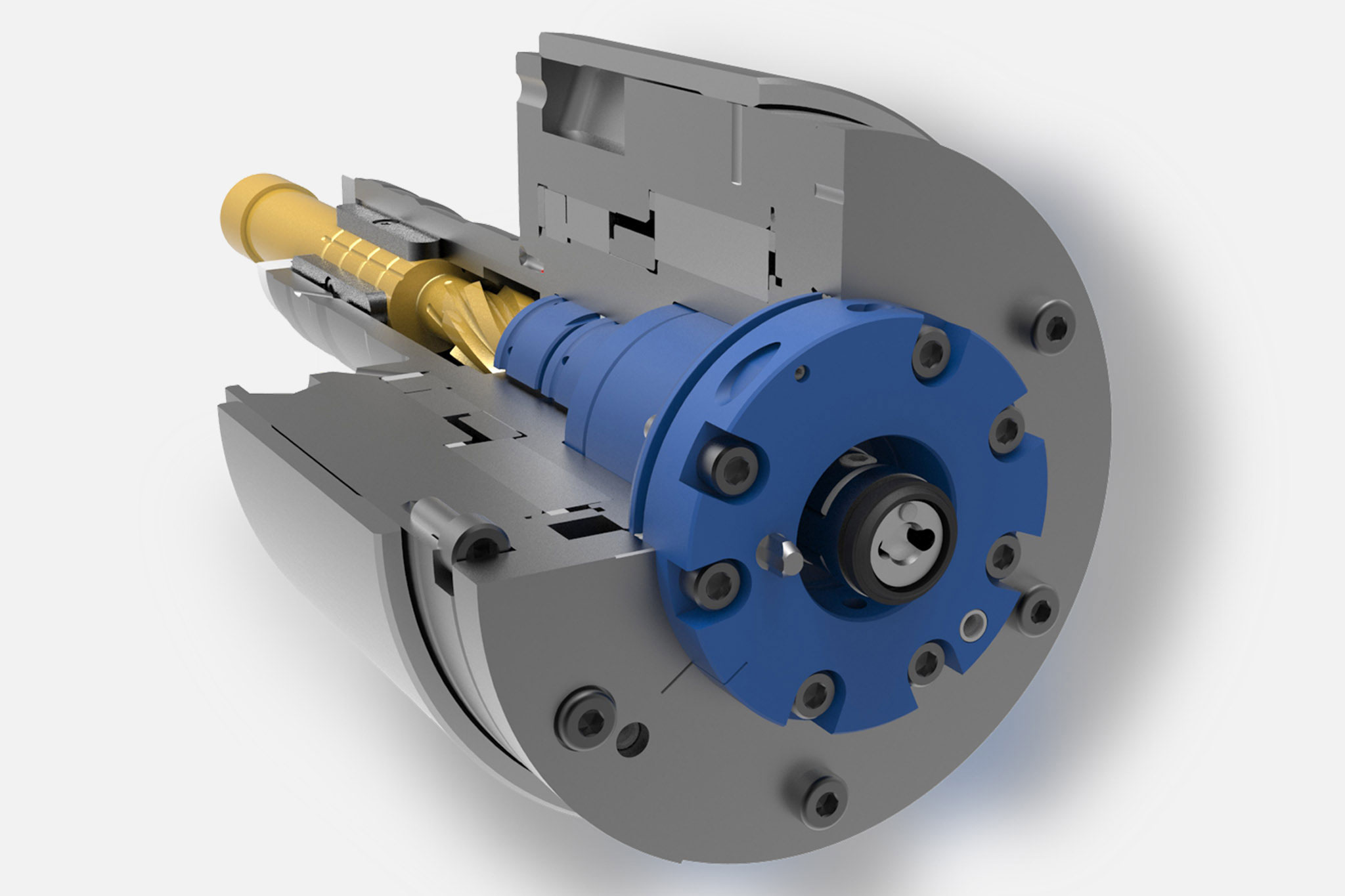
Le teste a sfacciare vengono impiegate per spiantaure, rettifiche a tuffo e lavorazione dei profili, principalmente nella grande produzione in serie su macchine speciali. L'azionamento di questi utensili a cursore e/o l'azionamento di supporto utensile e taglienti avviene mediante un'unità di trazione piana a comando NC, che si trova nell’allogiamento del mandrino o presso il lato posteriore dell'unità di avanzamento.
Le teste a sfacciare vengono impiegate per spiantaure, rettifiche a tuffo e lavorazione dei profili, principalmente nella grande produzione in serie su macchine speciali. L'azionamento di questi utensili a cursore e/o l'azionamento di supporto utensile e taglienti avviene mediante un'unità di trazione piana a comando NC, che si trova nell’allogiamento del mandrino o presso il lato posteriore dell'unità di avanzamento.
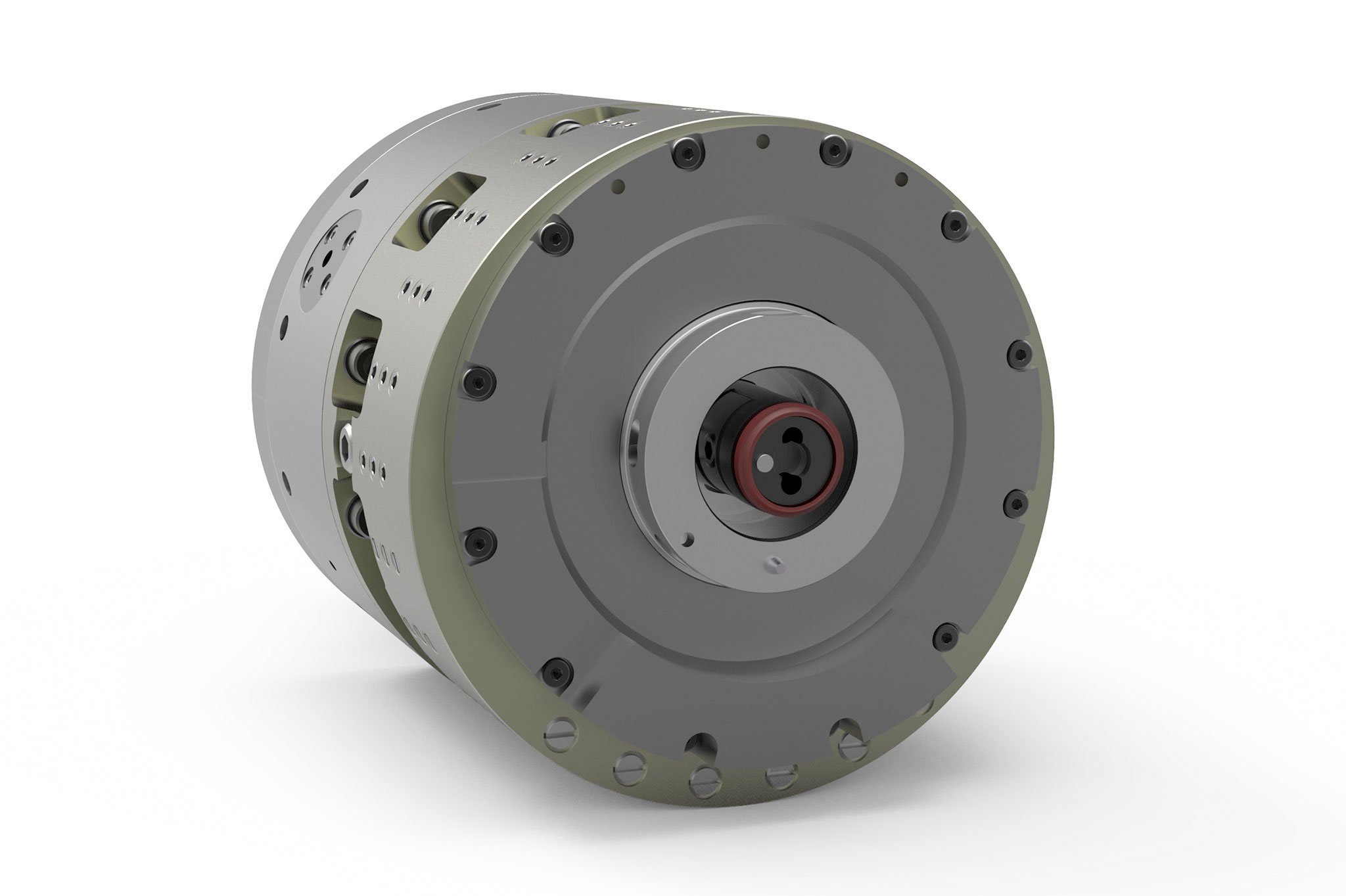
Il sistema di utensili meccatronico TOOLTRONIC
Tanto su un centro di lavorazione quanto su una macchina speciale, il sistema di utensili meccatronico TOOLTRONIC esegue movimenti di azionamento in modo semplice e affidabile. È così possibile sia la lavorazione di contorni, rettifiche a tuffo e forature non cilindriche che la realizzazione di circuiti di regolazione ad anello chiuso per la compensazione dei taglienti, oppure ancora la semplice produzione di serie di elementi in diverse varianti.
Il modulo di azionamento autonomo rappresenta un importante asse NC nell'unità di comando superiore della macchina grazie alla trasmissione induttiva dell’energia e alla trasmissione bidirezionale dei dati. In questo modo consente di sfruttare la piena funzionalità dei moderni comandi CNC anche in combinazione con il TOOLTRONIC.
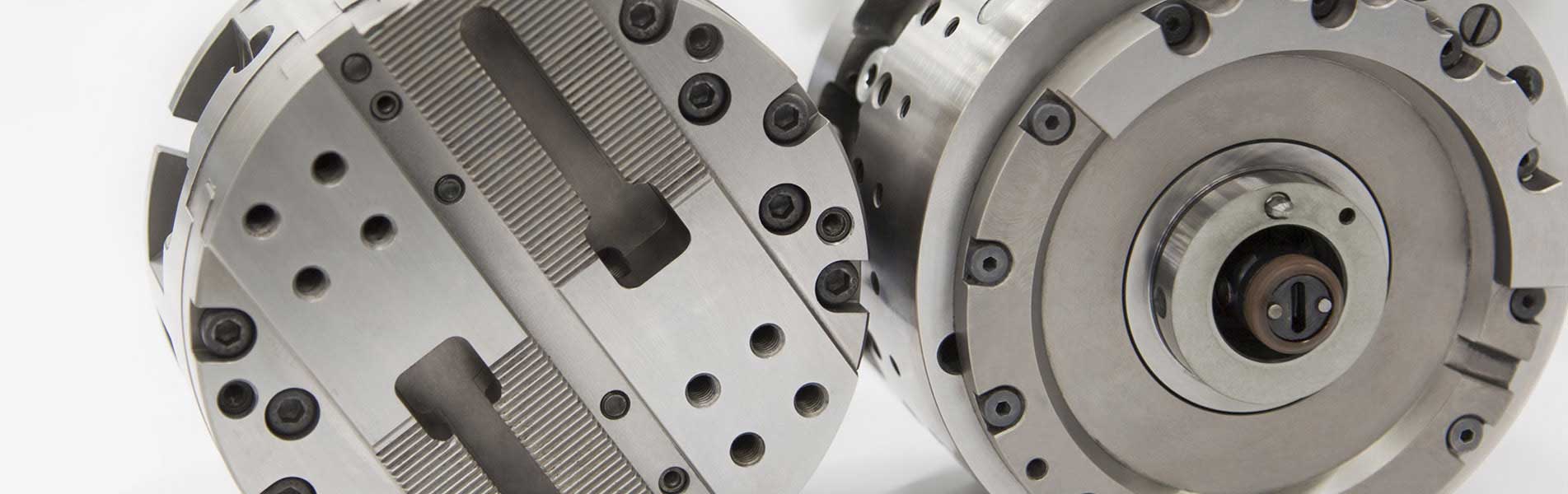
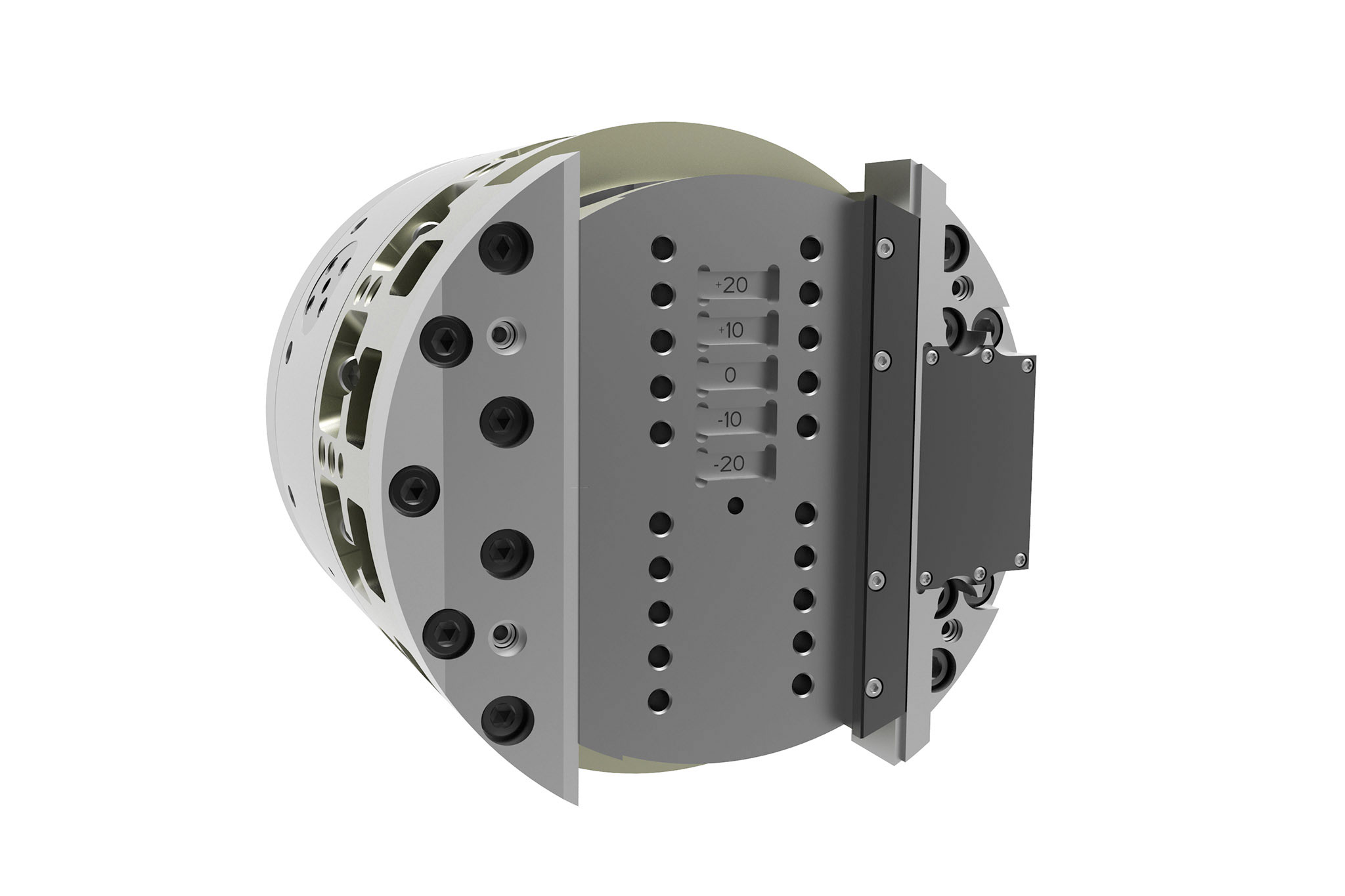
A seconda del compito di lavorazione, nell’interfaccia modulare di TOOLTRONIC vengono inserite diverse teste a sfacciare (lato uscita) di MAPAL. Come norma vengono impiegati utensili di azionamento eccentrici (EAT). Le applicazioni che richiedono una grande corsa con adattamento del numero di giri vengono coperte da utensili di azionamento lineari (LAT).
Il modulo di azionamento autonomo rappresenta un importante asse NC nell'unità di comando superiore della macchina grazie alla trasmissione induttiva dell’energia e alla trasmissione bidirezionale dei dati. In questo modo consente di sfruttare la piena funzionalità dei moderni comandi CNC anche in combinazione con il TOOLTRONIC.
A seconda del compito di lavorazione, nell’interfaccia modulare di TOOLTRONIC vengono inserite diverse teste a sfacciare (lato uscita) di MAPAL. Come norma vengono impiegati utensili di azionamento eccentrici (EAT). Le applicazioni che richiedono una grande corsa con adattamento del numero di giri vengono coperte da utensili di azionamento lineari (LAT).
Teste a sfacciare
Le teste a sfacciare vengono impiegate per spiantaure, rettifiche a tuffo e lavorazione dei profili, principalmente nella grande produzione in serie su macchine speciali. L'azionamento di questi utensili a cursore e/o l'azionamento di supporto utensile e taglienti avviene mediante un'unità di trazione piana a comando NC, che si trova nell’allogiamento del mandrino o presso il lato posteriore dell'unità di avanzamento.